Institute of Technology, Resource and Energy-efficient Engineering (TREE)
Our Understanding of Sustainability
Our Sustainability Vision

1. Research and education at TREE are guided by the principle of sustainability.
2. Our understanding of sustainability is based on the definition from Brundtland (1987), the elaborations in the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations (2015), as well as the detailed explanations provided by the Council for Sustainable Development and the German Sustainability Strategy.
3. TREE applies the concept of sustainability in a discipline-specific manner.

4. Sustainability in Research: TREE provides a platform for interdisciplinary and collaborative research that
- encompasses both sustainable technology development, considering sustainability criteria, and
- technology development for sustainable development (to achieve sustainability goals).
- Reflection and discourse are integral parts of research at TREE.
5. Sustainability in Education: TREE instructors convey sustainability in a discipline-specific manner by addressing the social, ecological, and economic consequences of technologies. Additionally, sustainability is reflected upon as a normative system.

6. Scientific reflection and collegial exchange characterize the discussions about sustainability orientation at TREE.
7. The public is kept informed about teaching and research activities at TREE.
8. The sustainability vision at TREE is collaboratively and participatively developed by researchers within TREE. The discourse on sustainability in research and education is ongoing and includes all interested parties.
„It is important for us to use old computers to demonstrate that one doesn't always need new hardware to advance research. These older machines can still be very useful to us, and we aim to continue using them until they truly reach the end of their operational life.”
Malte Pfennig - Ph.D. candidate and Research Associate in the TransHyDE-Sys-MechaMod project.

Selected Examples of Sustainable Practices at TREE
Second Life for Old Computers

Retired computers, formerly used in CAD rooms, are given a second life in our hydrogen laboratory. The computer is used here to store data from the laboratory equipment. These data are then sent to the computer via LAN and stored in a database. To save additional energy, further modifications were made: Both the CD drive and graphics card were removed because they were not required.
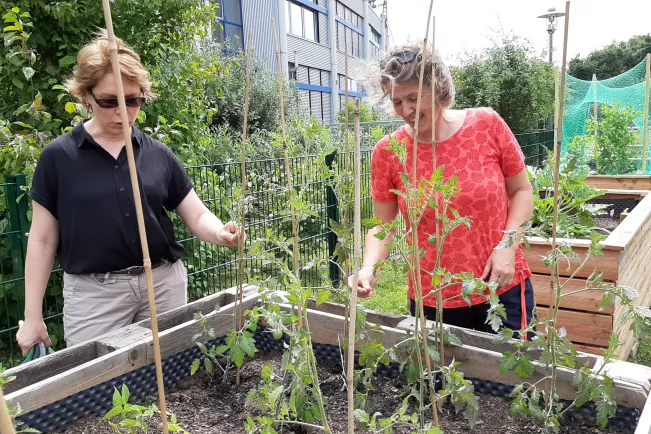
Campus Garden of H-BRS

Employees and students from TREE and H-BRS collaboratively create a campus garden, cultivate vegetables, and gather urban gardening experiences, ranging from planning and planting to harvesting and utilization. Recently, the garden was honored with the Environmental Award for Sankt Augustin. The project originated from a partnership between the Consumer Association of North Rhine-Westphalia (Verbraucherzentrale NRW) and Prof. Dr. Iris Groß.
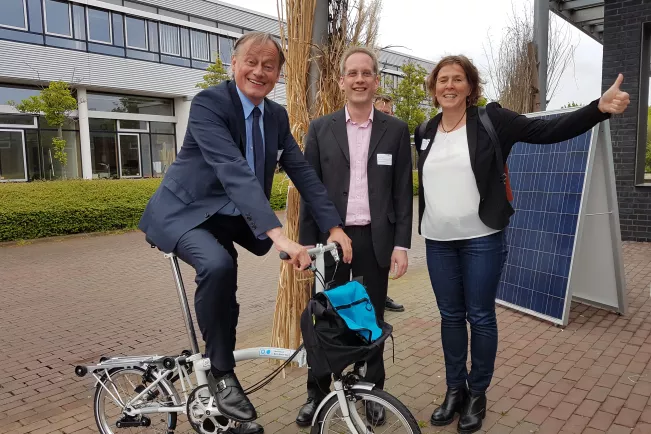
Folding Bicycle Rental for Business Trips
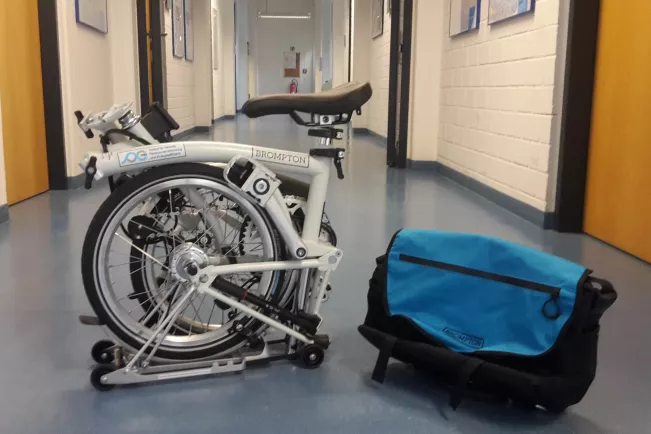

The TREE Institute offers its employees Brompton folding bicycles for rental during business trips. These bicycles can be folded into a compact suitcase size in a matter of seconds, making them ideal for combining with train travel during work-related journeys.