🎓Structure and Function of Organic Cation Transporters
Doctoral project at a glance
Departments and Instituts
Period
01.09.2024 to 31.08.2029
Project Description
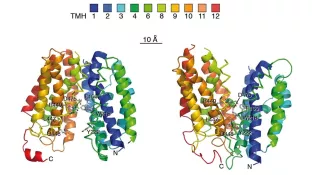
Organic cation transporters (OCTs) are members of the solute carrier transporter superfamily. The three main types are OCT1, OCT2 and OCT3, they are encoded by the genes SLC22A1, SLC22A2 and SLC22A3 respectively. OCTs are capable of bidirectional transport of various positively charged organic molecules, such as drugs, neurotransmitters and metabolic products.
Due to their ability to translocate structurally different compounds, OCTs contain a complex binding pocket with various interaction sites. However, the exact mode of substrate-transporter interactions for many compounds has not been resolved yet. Using site-directed mutagenesis, the substate-binding mechanisms of substrates can be resolved by functionally analyzing the generated mutants using electrophysiological techniques like two-electrode-voltage-clamp or solid supported membrane-based electrophysiology (SSME).
Anlaufstellen
Graduierteninstitut: Contact
Campus
Sankt Augustin
Room
F 427 , F 425, F 423
Opening hours
Mon-Fr 9.00 am-1.00 pm call us, send an e-mail or make an appointment for individual counselingfor

