Research at the university
Research Database: Projects
Forschungsprojekte (247)
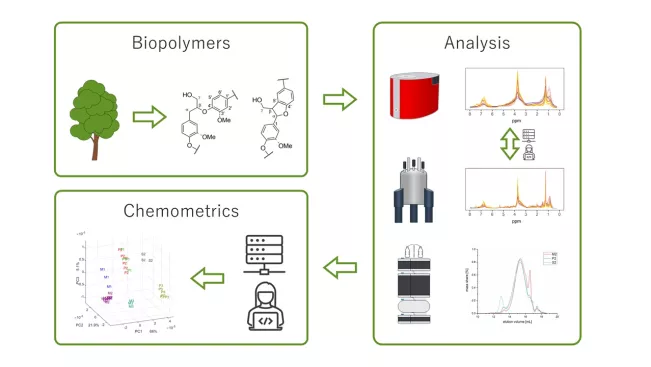
In the course of sustainable rethinking, it is extremely important to obtain chemical resources primarily from renewable raw materials. One possible candidate that can also be used in the long term in a wide variety of preliminary stages of the chemical industry is lignin. To this end, doctoral student Jonas Bergrath is examining various biogenic wastes (including waste wood and pomace from wine production) in order to isolate lignin that is as "green" as possible. Since lignin is extremely difficult to characterise and reproduce, he is using a wide range of analytical and computational chemistry methods to identify possible structure-property correlations. The overall goal is to link the physicochemical properties (including adsorption and behaviour in solvents) with structural elements of lignin and to use it as an adsorbent for small organic molecules (e.g. pharmaceuticals) in wastewater treatment.
Doctoral student XUAN TUNG DO is investigating how to turn a centuries-old waste product into a material with superpowers. Many everyday objects are still manufactured in some form from fossil raw materials such as petroleum. As these raw materials are only available in limited quantities, scientists are searching for sustainable alternatives. To this end, doctoral student Xuan Tung Do is investigating a waste product from the paper industry: lignin. Lignin is a complex biopolymer and must first be characterised using various analytical and statistical methods before it can be used as a direct substitute for petroleum. As part of his doctoral thesis, Do is determining the molecular weight of the biopolymer using various spectroscopic and 1D and 2D chromatographic methods.
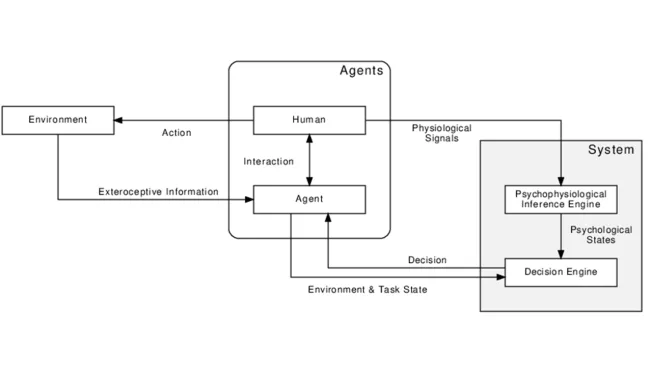
With the increasing prevalence of cognitive impairments, the importance of practical assistance systems that support people in the workplace is growing. The aim of the doctoral project of JORDAN SCHNEIDER is to develop an assistance system that uses wearable sensors to evaluate physiological signals in real time, assess cognitive stress levels and offer adaptive support. The aim is to demonstrate the potential of physiologically adaptive assistance systems in the workplace and thus promote the social participation of people with cognitive impairments in the labour market.
Extrusion blow moulding is one of the most economical processes for manufacturing thin-walled hollow plastic bodies, such as bottles, canisters or fuel tanks. After manufacture, cooling under moulding pressure causes shrinkage and distortion of the components. These undesirable deviations from the ideal geometry continue to pose a major problem for the blow moulding industry. In cooperation with the Dr. Reinold Hagen Foundation, doctoral student PATRICK MICHELS is working on the simulative prediction of material shrinkage and the associated component distortion. The focus of the doctoral project is the identification and calibration of a suitable material law to describe the complex time-, temperature- and process-dependent material behaviour of the polymer materials used. The improved models for shrinkage and distortion analysis will then be integrated into the standard CAE workflow for blow-moulded hollow plastic bodies.
The research work of ANGELA TURCK, initiated by the project "Diversity of Insects in Nature-Protected Areas (DINA)", analyses the complex links between agriculture and nature conservation. Since 2019, decisive changes have taken place: an increase in environmental awareness, political priorities in favour of environmental and climate protection, manifested, among other things, in the European "Green Deal" and the "Farm to Fork Strategy". At the same time, the COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced political decisions. In this dynamic context, the work emphasises the need for a stakeholder-centred approach. It analyses tensions and challenges for farmers in nature conservation areas. In addition, the study takes an in-depth look at the perspectives of farmers in order to understand their hesitations and aspirations in nature conservation. One focus is on analysing farmers' economic incentives for biodiversity using a motivation theory. The aim of the project is to thoroughly document the interactions between the main stakeholders and to develop solutions for sustainable coexistence through an integrative approach.
The Ghanaian healthcare sector suffers from an unstable power supply, which is often compensated for with diesel generators. However, in addition to the environmental and financial burden, this also poses a health risk to sick people and local residents. Renewable energy sources can help to ensure a clean and cost-effective energy supply, but they do pose risks to the stability of the power supply. PhD student Samer Chaaraoui is researching model predictive control for PV-diesel hybrid systems based on load and radiation forecasts. Various forecasting methods are being investigated, from simple statistical methods and numerical weather prediction models to the implementation of deep neural networks and artificial intelligence.
Engineering degree programmes in Germany are still heavily male-dominated. This underrepresentation of women is not just an individual problem, but also points to structural barriers that systematically impede the access and success of certain groups. VIVIEN MATHEIS' doctoral project addresses this issue by analysing the structural mechanisms of exclusion in engineering studies. It adopts an intersectional perspective of analysis that takes into account the interactions of various categories of difference (such as gender and class, race, etc.). The aim of the thesis is to develop university strategies based on the empirical findings that contribute to the opening up of engineering degree programmes and thus promote a more diverse student body in the long term.
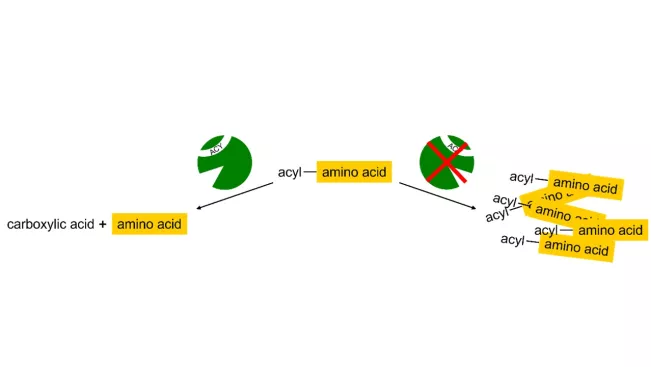
The doctoral project of LIL KLAAS aims to elucidate the molecular basis of inherited metabolic disorders caused by genetic variants in aminoacylase genes. These disorders can lead to severe neurological phenotypes in children, yet they remain poorly understood. A deficiency in one of the aminoacylase genes can result in the accumulation of N-acylated amino acids, primarily detectable in urine. To date, only the enzymatic functions of aminoacylases have been characterized, while their broader roles and potential interaction partners remain largely unknown. By investigating these aspects and gaining more detailed insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms, my research aims to provide a basis for potential improvements in diagnostics and treatment.
Biopolymers are becoming increasingly important in many medical and industrial applications. The use of raw materials such as lignin as a basis for industrial applications requires analytical methods to characterise their properties such as purity, composition and molecular weight. These properties fluctuate significantly in some cases and must therefore be continuously monitored. PhD student RENE BURGER is developing analytical methods that make this information accessible by combining molecular spectroscopic techniques such as infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with multivariate data analysis and modelling. These new methods represent fast and resource-efficient alternatives to conventional instrumental and wet-chemical techniques.
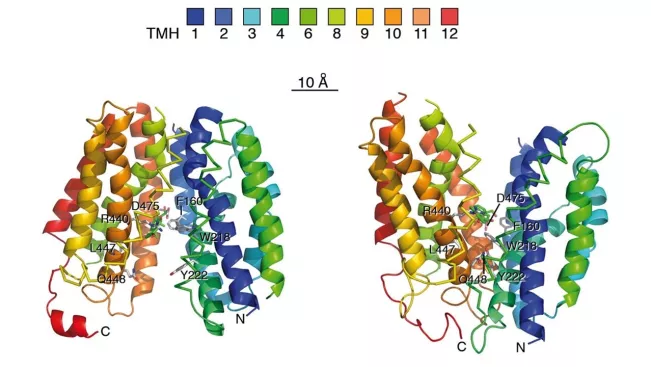
The project of PhD Candidate: YASEMIN AYLIN KEMPF deals with Organic cation transporters (OCTs) are proteins in our cells that move small, positively charged molecules, such as medicines, brain chemicals, and metabolic by-products. There are three main types: OCT1, OCT2, and OCT3. Since they can carry many different substances, their docking sites are quite complex, and scientists still don’t fully understand how these work. To find out more, parts of the transporter will be changed and then it is tested how these altered versions behave using special electrical measurement methods.
Contact Points
Centre for Science and Technology Transfer (ZWT)
Room
F 405
Vice President Research and Transfer
Campus
Sankt Augustin